Abstract
Research Article
Amine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Smart Nano Antibacterial Agent
Bagyalakshmi J*, Kalaimani S and Sowmiyadevi B
Published: 13 December, 2024 | Volume 8 - Issue 1 | Pages: 004-013
Conventional antibiotics are resisted by bacteria at an increasing rate, prompting studies into the development of alternate antibiotic agents. This work demonstrates the fabrication and characterization of amine functionalized graphene quantum dots (af-GQDs) with starting materials of graphene oxide, ammonia, and hydrogen peroxide by chemical oxidation and hydrothermal methods. The synthesized af-GQDs were characterized using analytical techniques such as UV-vis, fluorescence, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, and morphological studies through TEM. TEM images showed that af-GQDs have smooth surface morphology with porous in nature and are spherical in shape with particle size less than 20 nm. The prepared af-GQDs show a quantum yield of 26.32%. A growth inhibition test was performed on E. coli and S. aureus for the prepared af-GQDs at different increasing concentrations. The minimum inhibitory concentration for the prepared af-GQDs on
E. coli was found to be 55 μg/mL and for S. aureus was found to be 35 μg/mL. Percentage cell viability studies were performed on HeLa and Jukart cells for 24 hours at different concentrations. Both cells showed maximum cell viability percentage at the initial concentration. At higher concentrations, the cell viability is decreased for both cells but the Jukart cells show a minimum percentage of cell viability at higher concentrations than the HeLa cells.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.hor.1001029 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Quantum dot; Alternative antibiotic; Amine functionalization; ROS production
References
- Kadian S, Manik G, Das N, Nehra P, Chauhan RP, Roy P. Synthesis, characterization and investigation of synergistic antibacterial activity and cell viability of silver-sulphur doped graphene quantum dots (Ag@S-GQDs) nanocomposite. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8:3028-3037. Available from: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2020/tb/c9tb02823d
- Nichols F, Chen S. Graphene oxide quantum dot-based functional nanomaterials for effective antimicrobial applications. Chem Rec. 2020;20:1505-1515. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202000090
- Rajendiran K, Zhao Z, Pei DS, Fu A. Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of functionalized quantum dots. Polymers. 2019;11(10):1670. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101670
- Wong KK. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and its antibacterial property. Pal Yue-Kong Library: 2018;59. Available from: https://theses.lib.polyu.edu.hk/handle/200/9414
- Cheng L, Huang S, Wang X. Surface modification of graphene quantum dots and their biocompatibility in biomedical applications. Carbon. 2018;138:88-98..
- Habiba K, Bracho-Rincon DP, Gonzalez-Feliciano JA, Villalobos-Santos JC, Makarov VI, Ortiz D, et al. Synergistic antibacterial activity of PEGylated silver-graphene quantum dot nanocomposites. Appl Mater Today. 2015;80-87. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2015.10.001
- Yang J, Zhang X, Ma YH, Gao G, Chen X, Jia HR, et al. Carbon dot-based platform for simultaneous bacterial distinguishment and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(47):32170-32181. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10398
- Chen S, Quan Y, Yu YL, Wang JH. Graphene quantum dot/silver nanoparticle hybrids with oxidase activities for antibacterial application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(3):313-321. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00644
- Chhabra VA, Kaur R, Kumar N, Deep A, Rajesh C, Kim KH. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of functionalized graphene quantum dots with diverse fluorescence characteristics. RSC Adv. 2018;8:11446-11454. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01148F
- Wang Z, Xia J, Zhou C, Via B, Xia Y, Zhang F, et al. Synthesis of strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for drug carrier. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;112:192-196. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.07.025
- Iannazzo D, Pistone A, Ferro S, De Luca L, Monforte AM, Romeo R, Buemi MR, Pannecouque C, et al. Graphene quantum dots-based systems as HIV inhibitors. Bioconjug Chem. 2018;29(9):3084-3093. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00448
- Zhao M. Direct synthesis of graphene quantum dots with different fluorescence properties by oxidation of graphene oxide using nitric acid. Appl Sci. 2018;8(8):1303. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081303
- Tuerhong M, Yang X, Yin X-B. Review on carbon dots and their applications. Chin J Anal Chem. 2017;45(1):139-150. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.160295
- Arias LR, Yang LJ. Inactivation of bacterial pathogens by carbon nanotubes in suspensions. Langmuir. 2009;25(5):3003-3012. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/la802769m
- Liang J, Li W, Chen J, Huang X, Liu Y, Zhang X, et al. Antibacterial activity and synergetic mechanism of carbon dots against Gram-positive and -negative bacteria. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(9):6937-6945. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.1c00618
- Gao W, Thamphiwatana S, Angsantikul P, Zhang L. Nanoparticle approaches against bacterial infections. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2014;6(6):532-547. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1282
- Zhu Z, Bai Q, Li S, Li S, Liu M, Du F, et al. Antibacterial activity of graphene and graphene oxide. Small. 2020;16:2001440. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202001440
- Meziani MJ, Dong X, Zhu L, Jones LP, LeCroy GE, Yang F, et al. Visible-light-activated bactericidal functions of carbon "quantum" dots. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(17):10761-10766. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b01765
- Sun B, Wu F, Zhang Q, Chu X, Wang Z, Huang X, et al. Insight into the effect of particle size distribution differences on the antibacterial activity of carbon dots. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;584:505-519. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.015
- Xin Q, Shah H, Nawaz A, Xie W, Akram MZ, Batool A, et al. Antibacterial carbon-based nanomaterials. Adv Mater. 2019;31(45):e1804838. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201804838
- Dong X, Liang W, Meziani MJ, Sun YP, Yang L. Carbon dots as potent antimicrobial agents. Theranostics. 2020;10(2):671-686. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.39863
- Sun J, Yang S, Wang Z, Shen H, Xu T, Sun L, et al. Ultra-high quantum yield of graphene quantum dots: aromatic-nitrogen doping and photoluminescence mechanism. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization. 2015;32(4):434-430. Available from: http://www.seu-npc.com/publications/2015-Part.%20Part.%20Syst.%20Charact-Jing%20Sun.pdf
- Allen T. Particle size measurement. Springer; 2013 Nov 21. Available from: https://books.google.co.in/books/about/Particle_size_measurement.html?id=7dsFCAAAQBAJ&redir_esc=y
- Clogston JD, Patri AK. Zeta potential measurement. In: Characterization of nanoparticles intended for drug delivery. 2011:63-70. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-198-1_6
- Tang CY, Yang Z. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM). In: Membrane characterization. Elsevier; 2017:145-159. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63776-5.00008-5
- Kuo WS, Shao YT, Huang KS, Chou TM, Yang CH. Antimicrobial amino-functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for eliminating multidrug-resistant species in dual-modality photodynamic therapy and bioimaging under two-photon excitation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:14438-14446. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b01429
Figures:

Figure 1
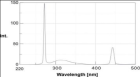
Figure 2
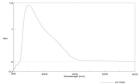
Figure 3
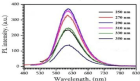
Figure 4
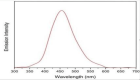
Figure 5
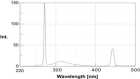
Figure 6
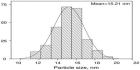
Figure 7

Figure 8
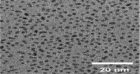
Figure 9

Figure 10
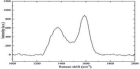
Figure 11
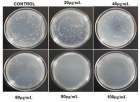
Figure 12
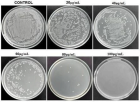
Figure 13
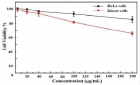
Figure 14
Similar Articles
-
Amine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Smart Nano Antibacterial AgentBagyalakshmi J*,Kalaimani S,Sowmiyadevi B. Amine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Smart Nano Antibacterial Agent. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.hor.1001029; 8: 004-013
Recently Viewed
-
Improving the Concrete Compressive and Flexural Strength with a Low Fraction Addition of Carboxylated Nitro-oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils from Banana RachisNgesa Ezekiel Mushi*, Emmanuel Kagya. Improving the Concrete Compressive and Flexural Strength with a Low Fraction Addition of Carboxylated Nitro-oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils from Banana Rachis. Ann Civil Environ Eng. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acee.1001072; 8: 087-095
-
Advancing Forensic Approaches to Human Trafficking: The Role of Dental IdentificationAiswarya GR*. Advancing Forensic Approaches to Human Trafficking: The Role of Dental Identification. J Forensic Sci Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001076; 9: 025-028
-
Toxic Components in Baby Care Products – A Comprehensive ReviewAvinav Jha*. Toxic Components in Baby Care Products – A Comprehensive Review. J Forensic Sci Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001077; 9: 029-036
-
Medicolegal Aspects of Deaths Due to Poisoning Occurred In Cities of Punjab and the State Of Himachal PradeshPancham Preet Kaur,Bhavish Prakash*. Medicolegal Aspects of Deaths Due to Poisoning Occurred In Cities of Punjab and the State Of Himachal Pradesh. J Forensic Sci Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001087; 9: 100-103
-
Computational Models in Systems and Synthetic Biology: Short OverviewMarian Gheorghe*. Computational Models in Systems and Synthetic Biology: Short Overview. Arch Biotechnol Biomed. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001037; 8: 001-002
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."